
Journal Name: Arthritis and Rheumatology
Overview
Arthritis and rheumatology are closely linked medical fields that focus on joint health and autoimmune disorders. While arthritis refers broadly to joint inflammation, rheumatology deals with diagnosing and treating rheumatic diseases—many of which involve arthritis. With millions of people affected globally, understanding these conditions is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is not a single disease but a term that encompasses over 100 types of joint-related disorders. The most common forms include osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
-
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease caused by the breakdown of cartilage due to aging or injury.
-
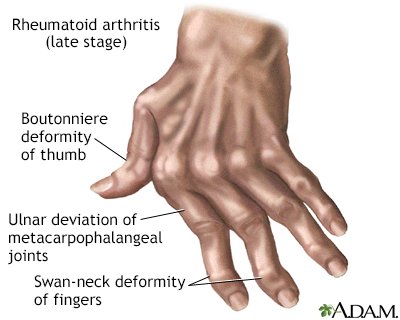
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling.
Other types include psoriatic arthritis, gout, and ankylosing spondylitis, each with unique symptoms and causes.
What is Rheumatology?
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases. These conditions often involve the joints, muscles, ligaments, and immune system. Rheumatologists are specialized doctors trained to handle complex autoimmune disorders such as:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
-
Lupus
-
Vasculitis
-
Scleroderma
-
Sjogren’s syndrome
Rheumatologists use a variety of diagnostic tools like blood tests, imaging (X-rays, MRI), and physical exams to identify the root cause of symptoms and develop personalized treatment plans.
Common Symptoms
Arthritis and rheumatic diseases can cause a wide range of symptoms, including:
-
Joint pain and stiffness
-
Swelling and redness
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Limited range of motion
-
Fever or weight loss (in autoimmune cases)
Early symptoms are often mild but can worsen over time if not properly treated. Early detection can help prevent permanent joint damage and improve quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of rheumatic diseases vary, but common contributing factors include:
-
Genetics
-
Age and gender (women are more prone to autoimmune disorders)
-
Infections
-
Injury or repetitive joint stress
-
Obesity
-
Smoking
Understanding your risk factors can help with early prevention and lifestyle adjustments.
Treatment and Management
Although there is no permanent cure for most forms of arthritis and autoimmune diseases, symptoms can be managed effectively. Treatment options include:
-
Medications: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, and biologics.
-
Physical therapy: Exercises to improve flexibility and strength.
-
Lifestyle changes: Healthy diet, weight loss, regular exercise, and stress management.
-
Surgical options: In severe cases, joint replacement or repair surgeries may be necessary.
About
Arthritis and rheumatology are closely related fields in medicine that deal with joint disorders and autoimmune conditions. These conditions affect millions of people worldwide, causing pain, inflammation, and reduced mobility. Understanding the link between arthritis and rheumatology is essential for early diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved quality of life.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a general term used to describe over 100 different types of joint diseases. The most common forms include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis typically causes joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. It can affect any joint in the body but most commonly impacts the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
-
Osteoarthritis (OA) is caused by wear and tear of the cartilage, usually due to aging or injury.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissue.
Other types of arthritis include psoriatic arthritis, gout, and lupus-related arthritis.
What Is Rheumatology?
Rheumatology is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on diagnosing and treating rheumatic diseases, including various forms of arthritis and autoimmune disorders. A rheumatologist is a medical doctor trained to treat conditions that affect the joints, muscles, and bones, as well as systemic autoimmune diseases like lupus, vasculitis, and scleroderma.
Rheumatologists use a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging to diagnose these complex conditions.
Common Symptoms of Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases
-
Persistent joint pain
-
Swelling and tenderness
-
Morning stiffness lasting longer than 30 minutes
-
Fatigue and general malaise
-
Limited movement in affected joints
-
Redness or warmth around joints
If you experience these symptoms for more than a few weeks, it’s crucial to consult a rheumatologist for proper evaluation.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact causes of many rheumatic diseases are still unknown, several risk factors have been identified:
-
Age: Risk increases with age, especially for osteoarthritis.
-
Genetics: Family history can influence susceptibility.
-
Gender: Women are more likely to develop autoimmune rheumatic diseases.
-
Obesity: Excess weight puts more stress on joints.
-
Infections and environmental triggers may also play a role in autoimmune reactions.
Treatment and Management
While there is no permanent cure for most types of arthritis, early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes. Treatment options include:
-
Medications: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, and biologic agents.
-
Physical therapy: To improve mobility and strength.
-
Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and weight management.
-
Surgery: Joint replacement may be recommended in severe cases.
Scope
When it comes to managing arthritis and autoimmune conditions, expert care makes all the difference. Scope Arthritis and Rheumatology is a leading medical facility dedicated to diagnosing, treating, and managing a wide range of rheumatic diseases. With a patient-centered approach and a commitment to cutting-edge treatment, Scope provides compassionate care for those suffering from chronic joint pain, inflammation, and systemic autoimmune conditions.
What is Rheumatology?
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases. These conditions often affect the joints, muscles, and bones, but can also involve internal organs. Common diseases treated by rheumatologists include:
-
Osteoarthritis
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
-
Lupus
-
Gout
-
Ankylosing spondylitis
-
Psoriatic arthritis
-
Vasculitis
-
Sjögren’s syndrome
Why Choose Scope Arthritis and Rheumatology?
1. Specialized Expertise:
Scope is home to board-certified rheumatologists with years of experience. Their deep understanding of autoimmune and musculoskeletal disorders ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plans.
2. Comprehensive Services:
From early-stage arthritis to complex autoimmune conditions, Scope offers a full spectrum of diagnostic and treatment services, including blood tests, imaging, infusion therapies, joint injections, and lifestyle counseling.
3. Personalized Care Plans:
No two patients are alike. Scope’s rheumatologists develop personalized care plans tailored to each individual’s symptoms, health history, and lifestyle. The goal is to reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall quality of life.
4. State-of-the-Art Technology:
The clinic uses advanced diagnostic tools and the latest treatment protocols to deliver world-class care. This includes biologic therapies, immunosuppressants, and innovative non-drug treatments.
Conditions Treated at Scope
Scope Arthritis and Rheumatology focuses on both common and rare rheumatic conditions. Some of the most frequently treated conditions include:
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A chronic inflammatory disorder that affects joints, often leading to pain and deformity.
-
Lupus: An autoimmune disease that can impact skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs.
-
Gout: A type of arthritis caused by uric acid buildup, leading to intense joint pain.
-
Fibromyalgia: A condition marked by widespread pain and fatigue, often misunderstood or misdiagnosed.
Patient-Centered Approach
Scope emphasizes education, communication, and collaboration. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in their treatment decisions. Regular follow-ups, lifestyle guidance, and support groups are part of the holistic care model.
Convenient Access and Insurance Support
Scope accepts most major insurance plans and offers flexible appointment scheduling. Whether you're dealing with newly developed symptoms or need ongoing management for a chronic condition, Scope makes it easy to get the care you need.