
Journal Name: Information Fusion
Overview
Title: Understanding Information Fusion: Concepts, Applications, and Benefits
Introduction to Information Fusion
Information Fusion is a multidisciplinary field that combines data from multiple sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source. With the explosion of big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and sensor technologies, Information Fusion has become an essential process in a wide range of industries—from defense and surveillance to healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems.
What is Information Fusion?
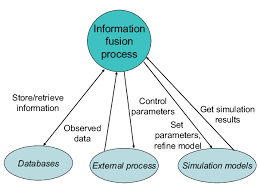
At its core, Information Fusion involves the integration of data from diverse sources such as sensors, databases, human input, or AI models. The goal is to reduce uncertainty and enhance decision-making by creating a unified and reliable representation of the underlying situation or environment.
There are various levels of Information Fusion, typically categorized as:
-
Data-Level Fusion: Raw data from multiple sources are combined before any processing.
-
Feature-Level Fusion: Features extracted from different sources are merged.
-
Decision-Level Fusion: Individual decisions or inferences are combined to reach a final conclusion.
Applications of Information Fusion
-
Defense and Security: In military operations, Information Fusion helps integrate intelligence from satellites, radars, and field agents to support strategic decision-making.
-
Healthcare: Fusion of medical records, diagnostic imaging, and sensor data enables better diagnosis and treatment plans.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on Information Fusion to merge data from cameras, LiDAR, GPS, and radar for safe navigation.
-
Finance: Banks and financial institutions use fusion techniques to combine market data, customer behavior, and economic indicators for risk assessment and fraud detection.
-
Smart Cities: Urban planning and public safety are enhanced through fusion of data from traffic sensors, CCTV, and social media feeds.
Benefits of Information Fusion
-
Improved Accuracy: By synthesizing data from multiple sources, fusion reduces noise and increases reliability.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: Fusion supports real-time, data-driven decisions in dynamic environments.
-
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: It optimizes resource usage by eliminating redundant or conflicting information.
-
Robustness and Fault Tolerance: Information Fusion systems can continue functioning even when some data sources fail or provide incorrect information.
Challenges in Information Fusion
Despite its advantages, Information Fusion comes with challenges such as data heterogeneity, scalability, real-time processing needs, and ensuring data privacy. Advanced techniques in machine learning, data mining, and distributed computing are helping to address these issues.
About
Understanding Information Fusion: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s data-driven world, Information Fusion plays a critical role in extracting actionable insights from multiple sources of information. Whether in defense, healthcare, business intelligence, or autonomous systems, the concept of information fusion is transforming the way organizations make decisions and respond to dynamic environments.
What is Information Fusion?
Information fusion refers to the process of integrating data from multiple sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source. The main objective is to improve situational awareness, reduce uncertainty, and support informed decision-making.
Information fusion systems are designed to handle data that may vary in format, accuracy, and reliability. By combining this data intelligently, these systems can deliver enhanced interpretations that are more comprehensive than isolated observations.
Key Levels of Information Fusion
Information fusion typically operates at three main levels:
-
Data-Level Fusion: Involves combining raw data from various sources. This level focuses on increasing signal-to-noise ratio and is often used in sensor networks.
-
Feature-Level Fusion: Extracted features from raw data are combined to enhance pattern recognition and classification.
-
Decision-Level Fusion: Involves combining decisions from multiple systems or algorithms to produce a final, improved decision output.
Applications of Information Fusion
Information fusion has a wide array of applications across industries:
-
Defense and Military: Used in surveillance, reconnaissance, and command-and-control systems to synthesize data from multiple sensors and sources for battlefield awareness.
-
Healthcare: Assists in diagnostics and treatment planning by integrating patient data from various medical devices and databases.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Combines inputs from cameras, LiDAR, radar, and GPS to help vehicles navigate safely and efficiently.
-
Cybersecurity: Enhances threat detection by correlating data from different monitoring systems and security logs.
-
Business Intelligence: Helps organizations integrate data from different departments to generate comprehensive performance insights.
Benefits of Information Fusion
-
Improved Accuracy: Combining multiple sources reduces the impact of noise or errors from any single source.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: Better insights lead to faster and more confident decisions.
-
Cost Efficiency: Streamlined data analysis can reduce operational costs by improving resource allocation.
-
Robustness and Reliability: Systems become more fault-tolerant by compensating for missing or faulty data.
Challenges in Information Fusion
Despite its benefits, information fusion faces several challenges:
-
Data Heterogeneity: Combining data from different formats and quality levels can be complex.
-
Real-Time Processing: Many applications require high-speed fusion for time-critical decisions.
-
Scalability: As the volume of data grows, systems must scale without compromising performance.
Scope
Scope of Information Fusion: Unlocking the Power of Data Integration
Information fusion is an emerging interdisciplinary field focused on integrating data from multiple sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source. As the volume of data grows exponentially across domains, the scope of information fusion becomes increasingly significant in areas ranging from defense and healthcare to finance and smart cities.
What is Information Fusion?
At its core, information fusion involves the process of combining data from various origins—such as sensors, databases, or user inputs—to make better decisions. This integration can be done at different levels: raw data level, feature level, or decision level. Techniques used include statistical methods, machine learning, neural networks, and fuzzy logic.
Applications of Information Fusion
One of the biggest strengths of multi-sensor data fusion lies in its versatility. It finds applications across a wide range of industries:
1. Defense and Surveillance
In military and homeland security, information fusion is used to integrate data from satellites, drones, and ground-based sensors. This enhances situational awareness, target tracking, and threat assessment.
2. Healthcare
Medical diagnostics benefit from fusing data from wearable devices, lab reports, imaging, and patient history. This leads to early detection, more accurate diagnoses, and personalized treatment plans.
3. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely heavily on information fusion by combining inputs from LIDAR, radar, GPS, and cameras. This integrated data allows for better decision-making in real-time navigation and obstacle avoidance.
4. Smart Cities
In urban planning and management, data from traffic sensors, weather stations, and utility grids are fused to optimize resource use, enhance public safety, and reduce energy consumption.
5. Finance and Business Intelligence
Fusion techniques help detect fraud, assess risk, and develop market forecasts by integrating diverse data streams such as transaction records, social media signals, and economic indicators.
Benefits of Information Fusion
-
Improved Accuracy: By leveraging multiple data sources, the final outcome is often more reliable.
-
Enhanced Robustness: Fusion reduces the risk of failure caused by faulty or missing data from a single source.
-
Faster Decision-Making: Real-time integration supports quicker responses in dynamic environments.
The Future of Information Fusion
As technology advances, the future of information fusion looks promising. Developments in artificial intelligence and big data analytics are expected to enhance the efficiency and intelligence of fusion systems. The integration of quantum computing and edge computing will further expand its capabilities in real-time and large-scale environments.
With the rise of IoT and 5G, the volume of available data will only increase, making information fusion even more vital for meaningful analysis and actionable insights.