
Journal Name: Hepatology
Overview
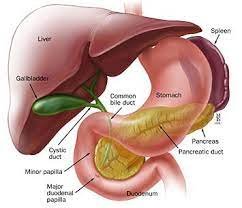
Hepatology is the branch of medicine focused on the study, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to the liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas. As one of the body's most important organs, the liver plays a crucial role in metabolism, detoxification, bile production, and various other vital functions. Hepatologists are specialists who dedicate their careers to understanding liver diseases and providing care to patients suffering from conditions such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and fatty liver disease.
The Importance of the Liver
The liver is the second-largest organ in the human body, responsible for a variety of essential functions. It detoxifies harmful substances, synthesizes proteins, produces bile to aid digestion, stores glycogen for energy, and regulates blood clotting. Given these roles, any disruption in liver function can lead to serious health complications, which is why the study of hepatology is so crucial.
Common Liver Diseases in Hepatology
-
Hepatitis: Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by viral infections, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Hepatitis B and C are particularly concerning due to their chronic nature and association with liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This is a condition in which fat accumulates in the liver without excessive alcohol consumption. It has become increasingly common due to the rise in obesity and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can progress to more severe forms, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to cirrhosis.
-
Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is the result of long-term liver damage that leads to scarring and impaired liver function. It can be caused by chronic hepatitis, excessive alcohol use, or other conditions such as NASH.
-
Liver Cancer: Primary liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), often develops in the setting of cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis infections. It is one of the most common cancers worldwide and is frequently diagnosed at advanced stages.
-
Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD): Chronic excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of liver damage. ALD can manifest in a range of forms, from fatty liver to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Advancements in Hepatology
Over the years, hepatology has seen significant advancements, particularly in the areas of diagnostics and treatment. The advent of antiviral therapies for hepatitis B and C has dramatically reduced the burden of these diseases, while improved imaging techniques like elastography and liver biopsies have enhanced the ability to assess liver damage and monitor disease progression.
One of the most notable breakthroughs in hepatology is the development of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) drugs for hepatitis C. These medications have revolutionized the treatment landscape, offering a cure for many patients who previously had limited options.
Additionally, liver transplantation has become an increasingly successful procedure for patients with end-stage liver disease, offering hope for those with cirrhosis or liver cancer that cannot be treated otherwise.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Prevention is a key focus in hepatology, and it involves lifestyle changes, vaccinations, and regular screenings. Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and getting vaccinated against hepatitis A and B can reduce the risk of liver disease. For individuals at risk of hepatitis C, screening and early detection are vital for effective treatment and disease management.
About
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases related to the liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas. It plays a crucial role in the management of liver disorders, which can range from mild conditions like fatty liver disease to more severe issues such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. With liver diseases becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide, hepatology has become a key area of research, diagnosis, and clinical care.
What is Hepatology?
Hepatology is a specialized field within internal medicine that deals with the liver and its associated organs. The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous essential functions, including detoxifying harmful substances from the blood, producing bile for digestion, and regulating metabolism. Given its importance, any dysfunction in the liver can lead to a wide range of health complications.
Hepatologists, who are doctors specializing in this field, manage and treat liver-related conditions. They are trained to perform diagnostic procedures like liver biopsies, endoscopic evaluations, and blood tests to assess liver function and identify diseases.
Common Liver Diseases Treated in Hepatology
Some of the most common liver conditions addressed in hepatology include:
-
Hepatitis: Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, typically caused by viral infections (e.g., Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C). Chronic hepatitis can lead to severe complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer if left untreated.
-
Fatty Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) are conditions where fat builds up in the liver. Both can progress to more serious liver damage if not properly managed.
-
Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is the scarring of the liver tissue, often due to chronic alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, or fatty liver disease. As cirrhosis progresses, it impairs liver function and can lead to life-threatening complications such as liver failure.
-
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma): This type of cancer originates in the liver and is often the result of chronic liver diseases like hepatitis and cirrhosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to improving outcomes.
-
Gallbladder and Biliary Tract Diseases: Hepatologists also treat conditions related to the gallbladder and bile ducts, such as gallstones and cholangitis.
Advances in Hepatology
Over the past few decades, there have been significant advancements in the field of hepatology, particularly in the treatment of viral hepatitis. The advent of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) has revolutionized the treatment of Hepatitis C, offering patients a cure with shorter treatment durations and fewer side effects.
Additionally, the growing focus on liver transplantation has improved the prognosis for patients with end-stage liver diseases. Hepatologists collaborate with transplant surgeons to provide life-saving interventions for patients in need of a liver transplant.
Preventing Liver Diseases
Prevention is an essential aspect of hepatology. Many liver diseases can be avoided or managed effectively with lifestyle changes and proper medical care. Some key preventive measures include:
-
Vaccination: Vaccines for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B are crucial in preventing these viral infections, especially in high-risk populations.
-
Healthy Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise can prevent or manage conditions like fatty liver disease, reducing the risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
-
Avoiding Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake can help prevent liver damage and reduce the risk of cirrhosis and other alcohol-related liver diseases.
-
Regular Screenings: People at risk of liver diseases, such as those with a family history of liver conditions or those with Hepatitis B or C, should undergo regular screenings to detect early signs of liver damage.
Scope
Hepatology, the branch of medicine that focuses on liver diseases, is a rapidly advancing field that plays a critical role in managing a wide range of conditions related to the liver, biliary system, and pancreas. The liver, being one of the most vital organs in the body, is responsible for several essential functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. As the incidence of liver-related diseases continues to rise globally, understanding the scope of hepatology becomes increasingly important for healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients alike.
Key Areas of Focus in Hepatology
-
Chronic Liver Diseases (CLD)
Chronic liver diseases are a major focus of hepatology. These include conditions such as cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis B and C, and fatty liver disease (NAFLD and NASH). Chronic liver diseases are often asymptomatic in their early stages, making early detection crucial for effective management. Hepatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating these conditions, aiming to prevent progression to liver failure and reduce the risk of liver cancer. -
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation is a lifesaving procedure for patients with end-stage liver disease, often due to cirrhosis or acute liver failure. The demand for liver transplants continues to grow, and advancements in transplantation techniques, immunosuppressive therapy, and organ preservation have improved patient outcomes. Hepatology plays a central role in the pre-transplant assessment, post-transplant care, and management of potential complications. -
Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis, particularly hepatitis B and C, remains a global health concern. Hepatologists are at the forefront of diagnosing and managing these infections, which can lead to severe liver damage if left untreated. The development of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapies for hepatitis C has revolutionized treatment, offering high cure rates with minimal side effects. Vaccines for hepatitis B have also made significant strides in preventing infection. -
Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD/NASH)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are rapidly emerging as leading causes of liver-related morbidity. These conditions are strongly linked to metabolic syndrome, including obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Hepatologists are increasingly involved in the diagnosis, management, and development of therapeutic strategies for these conditions, as they can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. -
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a primary liver cancer that often develops in the setting of chronic liver disease, especially in cirrhosis. Early detection is critical, and hepatologists use advanced imaging techniques, biopsy procedures, and serum biomarkers to diagnose HCC at an early stage. In addition to surgical resection and liver transplantation, innovative treatments such as locoregional therapies and systemic therapies are being utilized to improve patient outcomes. -
Biliary Diseases
Disorders of the bile ducts, such as primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), are also key areas of focus in hepatology. These autoimmune diseases can lead to progressive liver damage and liver failure. Hepatologists work on managing these conditions, utilizing medications to slow disease progression and providing support for patients with end-stage liver disease.
Advancements and Challenges in Hepatology
The field of hepatology has made tremendous progress in recent years. Advances in molecular biology, genomics, and imaging technologies have improved our understanding of liver diseases and have paved the way for more targeted therapies. However, challenges remain, including the need for improved screening methods, access to healthcare in low-resource settings, and the rising burden of liver diseases due to lifestyle factors like obesity and alcohol consumption.