
Journal Name: Gastroenterology
Overview
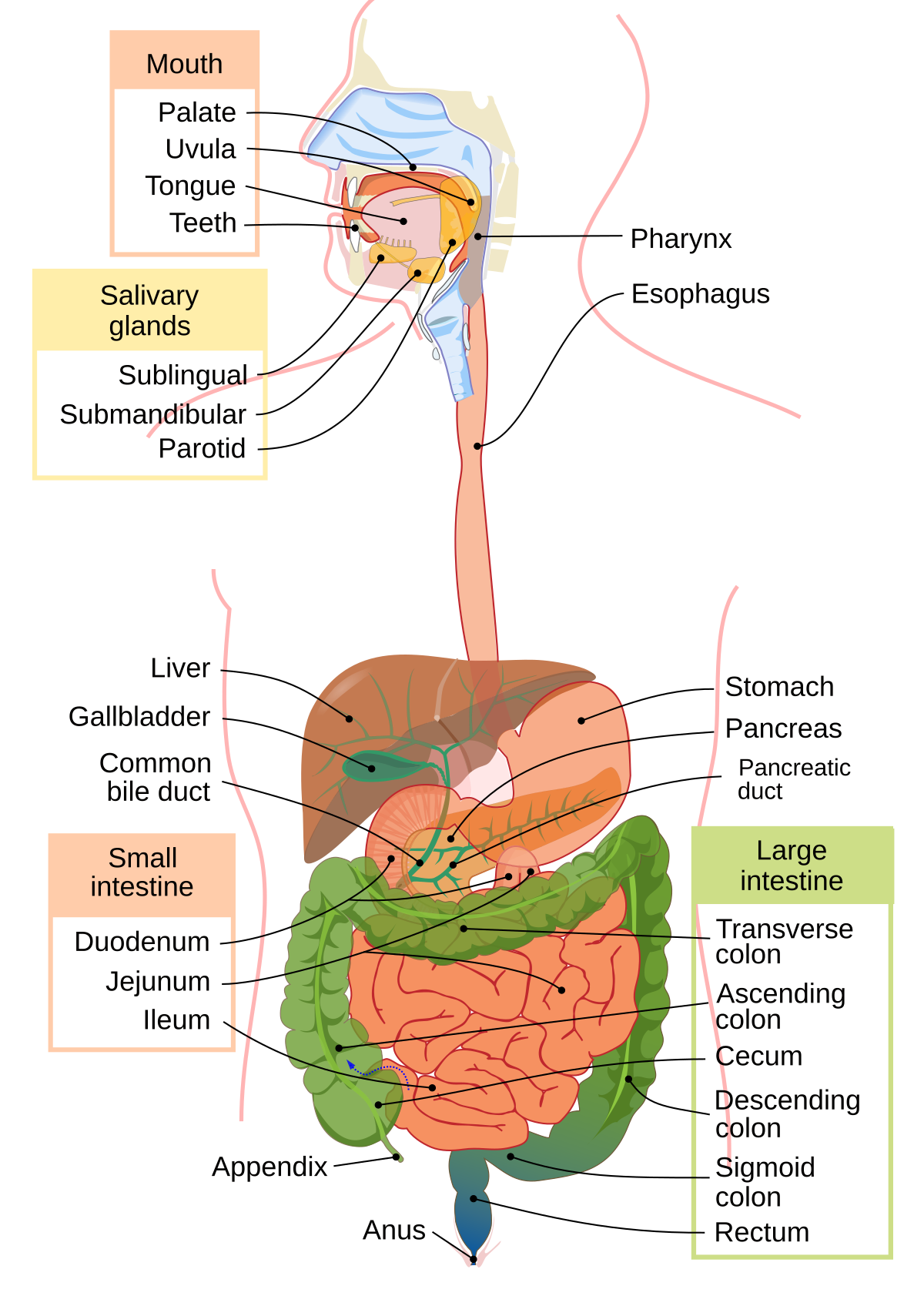
Gastroenterology is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the health of the digestive system, or the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This field encompasses the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases affecting the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Gastroenterologists are medical experts who help patients maintain digestive health, manage chronic conditions, and improve overall quality of life.
What Does a Gastroenterologist Do?
Gastroenterologists are trained to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions such as acid reflux (GERD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ulcers, celiac disease, gallstones, and liver disorders including hepatitis. They also perform essential procedures like endoscopies and colonoscopies, which allow for the visualization and treatment of internal issues without the need for surgery.
These procedures are crucial for detecting abnormalities like polyps, tumors, or signs of internal bleeding. Early detection can often lead to more effective treatment and even prevent serious conditions such as colorectal cancer.
Common Symptoms Requiring Gastroenterological Care
If you're experiencing persistent digestive issues, it may be time to see a gastroenterologist. Common symptoms include:
-
Abdominal pain or discomfort
-
Chronic constipation or diarrhea
-
Heartburn or acid reflux
-
Blood in the stool
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Difficulty swallowing
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more severe health issues, making early intervention essential.
Importance of Digestive Health
A healthy digestive system plays a key role in overall well-being. It’s responsible for absorbing nutrients, eliminating waste, and supporting the immune system. Poor digestive health can lead to fatigue, nutritional deficiencies, and a weakened immune response. With lifestyle changes, proper diet, and medical guidance, many gastrointestinal problems can be effectively managed or even prevented.
Advancements in Gastroenterology
Recent advancements in gastroenterology include non-invasive diagnostic tools, improved imaging technology, and innovative treatments for chronic conditions. Telemedicine has also made it easier for patients to consult specialists from the comfort of their homes. These improvements enhance patient outcomes and help doctors tailor treatments to individual needs.
When to See a Gastroenterologist
If you have a family history of GI disorders or you're over the age of 45, regular screenings such as colonoscopies are recommended. Early detection of colon cancer, for instance, significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
About
Gastroenterology is a branch of medicine that focuses on the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases related to the digestive system. This encompasses the entire digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, and includes the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. In recent years, the importance of maintaining optimal digestive health has gained significant attention due to its vital role in overall well-being.
What Does a Gastroenterologist Do?
A gastroenterologist is a medical professional specializing in the digestive system. They are experts in diagnosing and treating various conditions related to the digestive tract, such as acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, hepatitis, and colorectal cancer. They use a variety of diagnostic tools, including endoscopy, colonoscopy, and imaging techniques, to examine the digestive system and identify underlying issues. Once diagnosed, they recommend personalized treatment plans to manage and alleviate symptoms, which can range from dietary changes and medications to advanced surgical procedures.
Common Gastrointestinal Disorders
There are several gastrointestinal disorders that affect people worldwide, and understanding these conditions is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Some of the most common gastrointestinal disorders include:
-
Acid Reflux (GERD): Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid frequently leaks into the esophagus, causing heartburn, chest pain, and other discomforting symptoms. If left untreated, GERD can lead to more serious health problems such as esophageal ulcers or cancer.
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a chronic condition characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation. While the exact cause is unknown, stress and certain foods may trigger IBS symptoms.
-
Crohn’s Disease: Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and severe abdominal pain. It can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract and can result in complications such as bowel blockages.
-
Colorectal Cancer: Colorectal cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. It often develops from precancerous growths called polyps in the colon or rectum. Early detection through screening methods such as colonoscopies can greatly improve survival rates.
-
Liver Diseases: Conditions like hepatitis, fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis can severely affect liver function, which is vital for detoxification, digestion, and nutrient absorption.
The Role of Diet in Digestive Health
Diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help prevent many common digestive issues, such as constipation and acid reflux. Drinking plenty of water, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and limiting processed foods are also essential for digestive health. Additionally, understanding food intolerances and allergies can help prevent discomfort and manage conditions like IBS or celiac disease.
Scope
Gastroenterology is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of digestive system disorders. This field encompasses a wide range of conditions affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. As digestive health is integral to overall well-being, the scope of gastroenterology is vast and covers numerous aspects of patient care, research, and innovation.
What Does Gastroenterology Include?
The scope of gastroenterology spans both medical and procedural aspects. It addresses conditions from common issues like acid reflux to more severe diseases such as Crohn’s disease and liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterologists specialize in providing care for patients experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
1. Gastrointestinal Disorders: Gastroenterology deals with a variety of disorders that impact the digestive system, including:
-
Acid Reflux (GERD): A condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential damage to the lining of the esophagus.
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional GI disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): This includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract.
-
Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder where ingestion of gluten damages the small intestine lining.
2. Liver and Pancreatic Diseases: Gastroenterologists also focus on conditions related to the liver and pancreas, such as:
-
Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver caused by viral infections, alcohol use, or certain medications.
-
Liver Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver tissue often due to chronic liver disease, which can lead to liver failure.
-
Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, often caused by gallstones or alcohol abuse.
3. Colorectal Diseases: Colorectal issues form a significant part of gastroenterology. These include:
-
Colon Cancer: A major health concern, often preventable through early screening and regular check-ups.
-
Diverticulitis: Inflammation or infection of small pouches that can form in the colon walls.
-
Hemorrhoids: Swollen veins in the rectal area that can cause discomfort and bleeding.
4. Diagnostic Procedures: A key component of gastroenterology involves diagnostic procedures that allow for accurate assessment and treatment planning. These include:
-
Endoscopy: A procedure used to examine the inside of the GI tract using a flexible tube with a camera.
-
Colonoscopy: A specialized endoscopic procedure to examine the colon and detect abnormalities like polyps or cancer.
-
Liver Biopsy: A procedure to assess liver function and diagnose liver diseases.
5. Preventive Care and Screening: Gastroenterologists play a crucial role in preventing GI diseases through early detection and screening. Colon cancer screening is vital for individuals over 50, as early detection can significantly reduce mortality rates. Additionally, regular check-ups help identify liver diseases or digestive issues at an early stage, ensuring prompt intervention.
Emerging Trends in Gastroenterology
The field of gastroenterology has witnessed significant advances in recent years. New technologies, improved diagnostic tools, and novel therapies have revolutionized the way gastrointestinal diseases are managed. The emergence of biologic treatments for conditions like IBD has changed the landscape of disease management, providing patients with better long-term outcomes. Furthermore, advancements in minimally invasive procedures have improved recovery times and reduced the risks associated with surgeries.